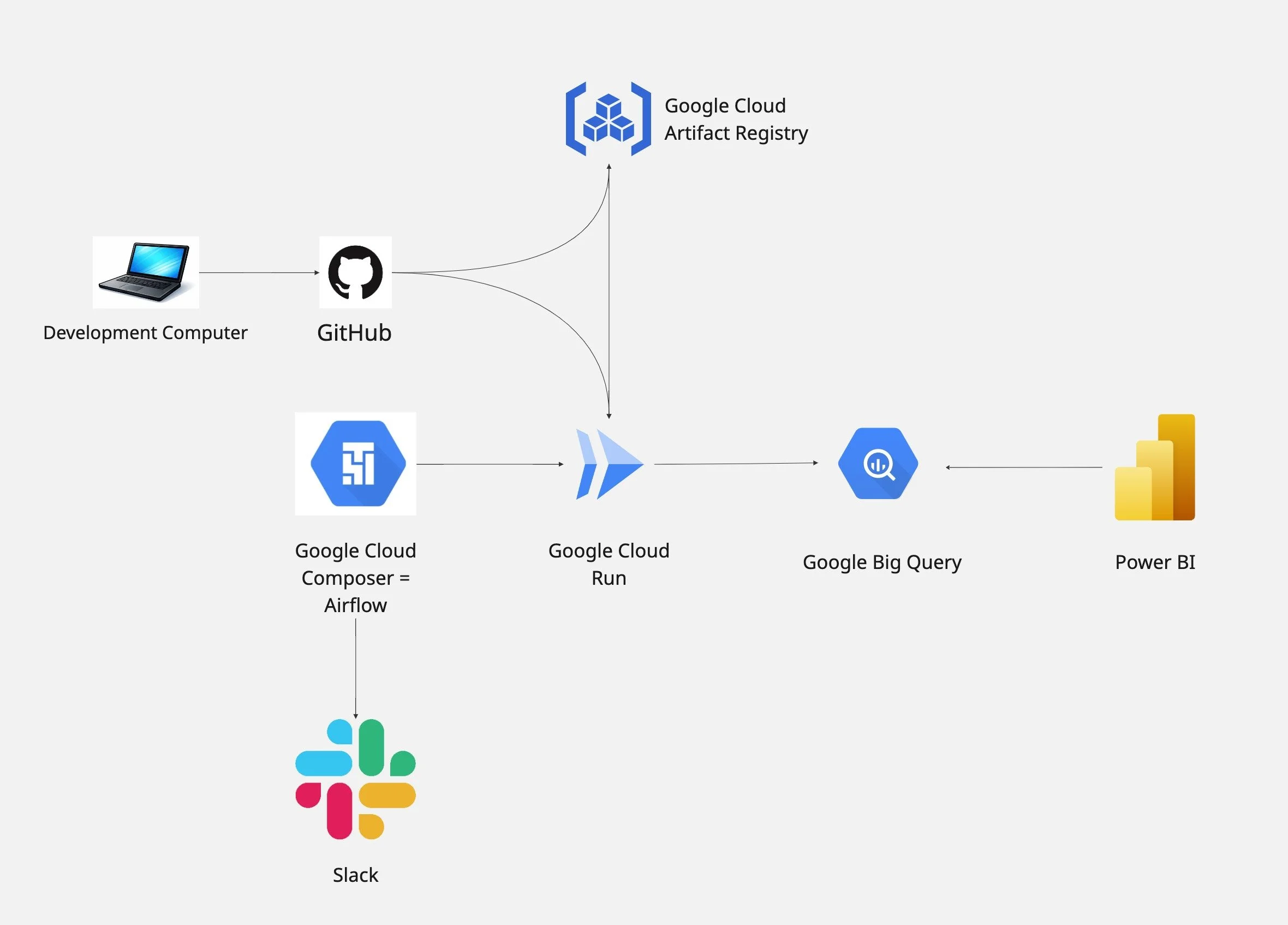
DBT on Google Cloud Platform: Infrastructure
On the left you can see my DBT on Google Cloud Platform Project Infrastructure Workflow
Below is a youtube video of me doing a demo of the infrastructure.
And below the video you can find an article on the topic.
Thank you for you attention in advance!
FROM DBT LOCALLY TO DBT IN THE CLOUD.
It all starts with my computer where I develop the DBT project locally being authenticated with Big Query through the google cloud sdk. You can find the DBT project files on by GitHub: https://github.com/Gregory-Bagramyan/dbt-gcp-project
I will go over the DBT files and logic in another article, this one focuses solely on the infrastructure.
So after I finished the development of DBT on my local computer I push the changes to GitHub from there GitHub does two things:
It pushes the Docker Image of the folder (DBT project files) to Artifact Registry (which is basically a library / storage for Docker Images)
It updates Cloud Run (service that can run Docker Containers from Images) to use the new Image from Artifact Registry.
This works because of:
A Dockerfile: https://github.com/Gregory-Bagramyan/dbt-gcp-project/blob/main/Dockerfile
A GitHub Actions workflow yaml file: https://github.com/Gregory-Bagramyan/dbt-gcp-project/blob/main/.github/workflows/dbt-cloud-run.yml
What happens is that on push to main, GitHub uses the yaml file above to execute a series of actions including building the Docker Image of the DBT project using the Dockerfile. Once the Image is built, it is sent to Artifact Registry and Cloud Run is updated to use this new Image.
The Dockerfile installs specific version of dbt-core and dbt-big-query, copies all the files in the dbt project folder and runs”dbt deps”, “dbt seeds” (because for this project the raw data lives in a csv file but for a real word project the data would probably be in the raw layer of the database) and “dbt build”.
The GitHub workflow authenticates to Google Cloud using a json key file and a service account dedicated to this workflow. The json key is stored in GitHub environment variables and the service account permissions are the following:
- Artifact Registry Attachment Writer
- Artifact Registry Writer
- Cloud Run Admin
- Cloud Run Invoker (for testing)
And Cloud Run uses it’s own service account with the following permissions:
- Big Query Data Editor
- Big Query Job User
TRIGGERING DBT BUILD ON A SCHEDULE
Now the DBT project lives as a Docker Image in Artifact Registry and is run as a Docker Container with Cloud Run when triggered. We now need to trigger Cloud Run on a schedule.
To do so we could have chosen Cloud Scheduler but I chose to work with Airflow (Cloud Composer on Google Cloud) to leverage it’s failure handling capacity and send a slack message on a DBT test failure for example.
Here is the airflow DAG python file I used: https://github.com/Gregory-Bagramyan/airflow-for-dbt-gcp-project/blob/main/dbt_build.py
It triggers Cloud Run at 2 am UTC everyday and alerts Slack in case of a failure.
Cloud Composer uses it’s own service account with the following permissions:
- Cloud Run Invoker
- Cloud Run Viewer
- Composer Worker
- Logs Writer
- Storage Object Admin
VISUALIZING THE DATA
Finally we will visualize the data using Power BI. All we need to do is connect Power BI to our Big Query project and start creating visualizations.
The service account used for this connection has the following permissions:
Big Query Data Viewer
Big Query Job User
Big Query Read Session User
Big Query User
Note: I tried using Looker and Looker Studio but it didn’t work with my GCP free trial.